Alopecia areata is a condition that causes hair to fall out in small patches, which can be unnoticeable. These patches may connect, however, and then become noticeable. The condition develops when the immune system attacks the hair follicles, resulting in hair loss. Sudden hair loss may occur on the scalp, and in some cases the eyebrows, eyelashes, and face, as well as other parts of the body. It can also develop slowly and recur after years between instances.
1)The main symptom of alopecia areata is hair loss. Hair usually falls out in small patches
on the scalp. These patches are often several centimeters or less.
2)Hair loss might also occur on other parts of the face, like the eyebrows, eyelashes, and
beard, as well as other parts of the body. Some people lose hair in a few places. Others
lose it in a lot of spots.
3)You may first notice clumps of hair on your pillow or in the shower. If the spots are on
the back of your head, someone may bring it to your attention. However, other health
conditions can also cause hair to fall out in a similar pattern. Hair loss alone isn’t
used to diagnose alopecia areata.
In rare cases, some people may experience more extensive hair loss. This is usually an
indication of another type of alopecia, such as:
1)Alopecia totalis, which is the loss of all hair on the scalp
2)Alopecia universalis, which is the loss of all hair on the entire body
3)The hair loss associated with alopecia areata is unpredictable and, as far as doctors
and researchers can tell, appears to be spontaneousTrusted Source. The hair may grow
back at any time and then may fall out again. The extent of hair loss and regrowth
varies greatly from person to person.
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition. An autoimmune condition develops when the immune system mistakes healthy cells for foreign substances. Normally, the immune system defends your body against foreign invaders, such as viruses and bacteria. If you have alopecia areata, however, your immune system mistakenly attacks your hair follicles. Hair follicles are the structures from which hairs grow. The follicles become smaller and stop producing hair, leading to hair loss. Researchers don’t know the exact cause of this condition. However, it most often occurs in people who have a family history of other autoimmune conditions, such as type 1 diabetes or rheumatoid arthritis. This is why some scientists suspect that genetics may contribute to the development of alopecia areata. They also believe that certain factors in the environment are needed to trigger alopecia areata in people who are genetically predisposed to it.
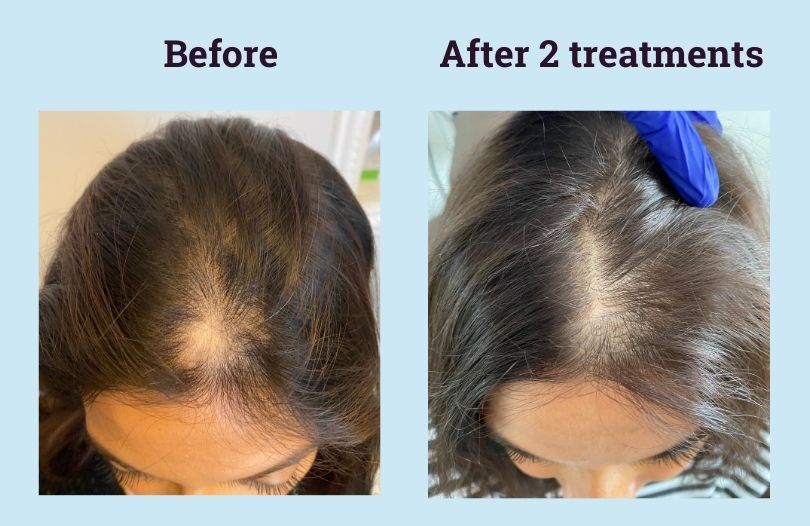
There’s no known cure for alopecia areata, but there are treatments that you can try that might be able to slow down future hair loss or help hair grow back more quickly. The condition is difficult to predict, which means it may require a large amount of trial and error until you find something that works for you.
Medical treatment:Topical agents: Minoxidil (Rogaine) is available OTC and applied twice daily to the scalp, eyebrows, and beard. It’s relatively safe, but it can take a year to see results. Anthralin (Dritho-Scalp) is a drug that irritates the skin in order to spur hair regrowth.
Injections:
Steroid injections are a common option for mild, patchy alopecia to help hair grow back on
bald spots. Tiny needles inject the steroid into the bare skin of the affected areas.
Oral treatments:
Cortisone tablets are sometimes used for extensive alopecia, but due to the possibility of
side effects, you should discuss this option with a doctor.
Some people with alopecia areata choose alternative therapies to treat the condition.
These may include:
1)Aromatherapy
2)Acupuncture
3)Microneedling
4)Probiotics
5)Low-level laser therapy (LLLT)
6)Vitamins, like zinc and biotin
7)Aloe vera drinks and topical gels
8)Onion juice rubbed onto the scalp
9)Essential oils like tea tree, rosemary, lavender, and peppermint
other oils, like coconut, castor, olive, and jojoba
10)An “anti-inflammatory” diet, also known as the “autoimmune protocol,” which is a restrictive diet that mainly includes meats and vegetables
scalp massage
11)Herbal supplements, such as ginseng, green tea, Chinese hibiscus, and saw palmetto

 She
Care
She
Care